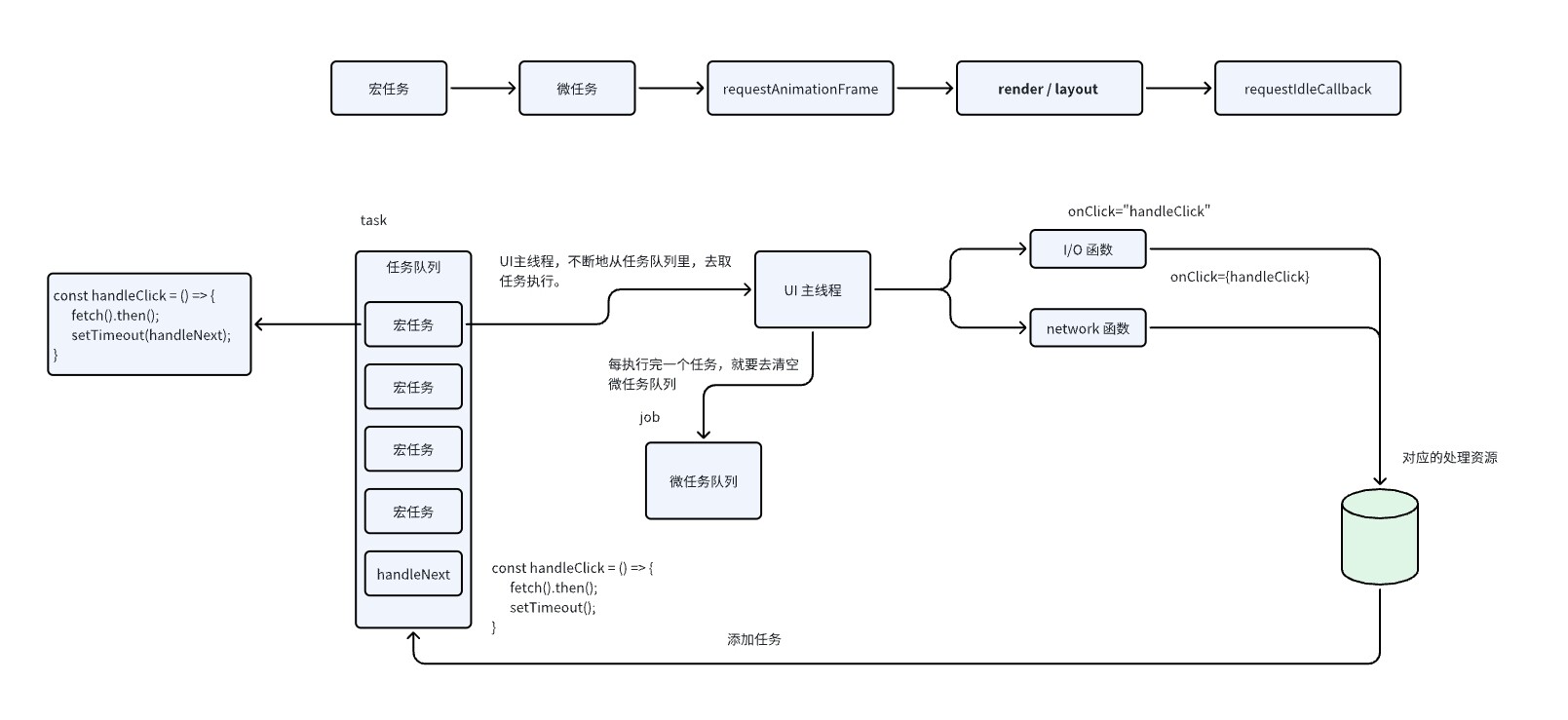
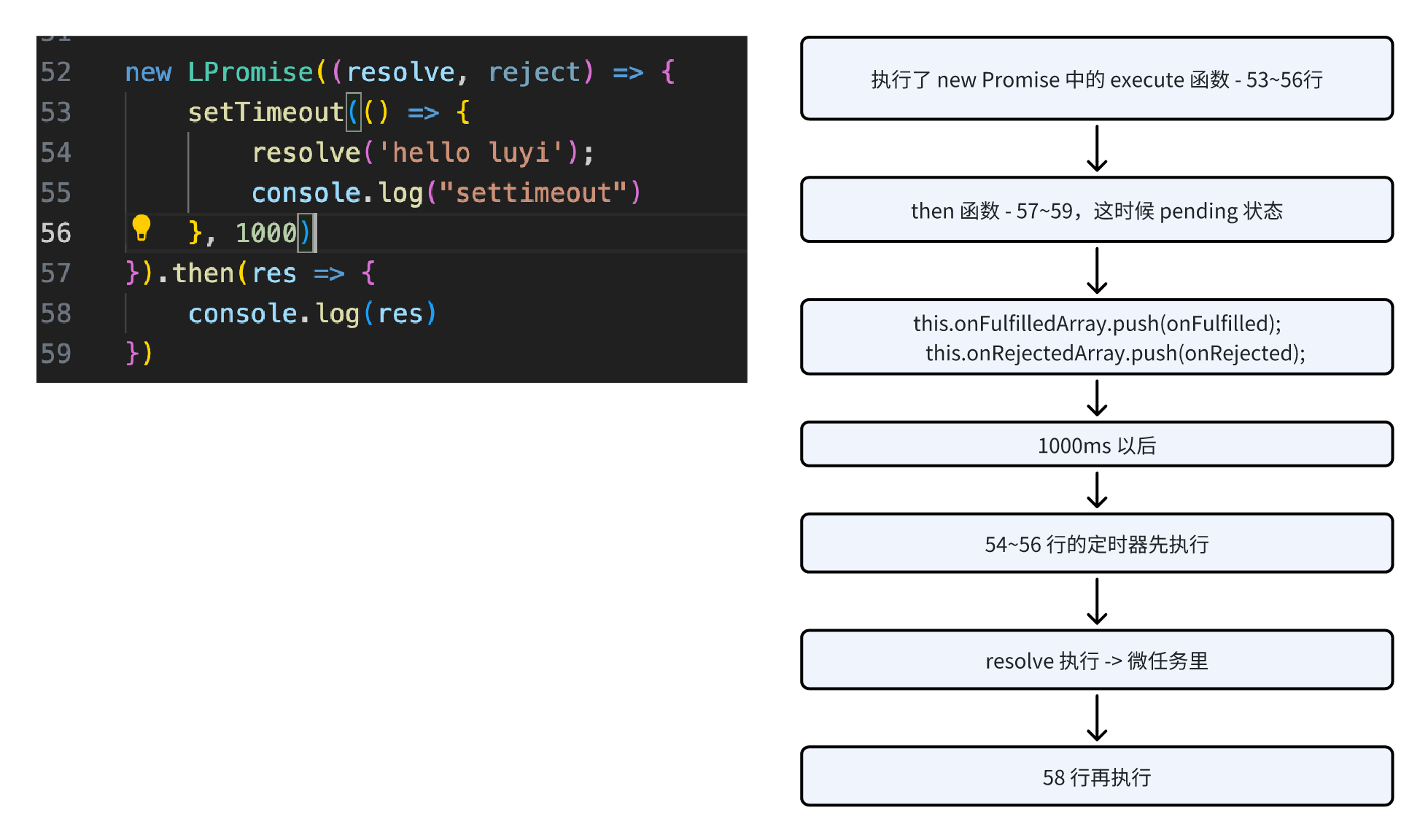
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
| const resolvePromise = (promise2, result, resolve, reject) => {
if (result === promise2) {
reject(new TypeError('error due to circular reference'))
}
let consumed = false
let thenable
if (result instanceof LPromise) {
if (result.status === 'pending') {
result.then(function (data) {
resolvePromise(promise2, data, resolve, reject)
}, reject)
} else {
result.then(resolve, reject)
}
return
}
let isComplexResult = (target) => (typeof target === 'function' || typeof target === 'object') && target !== null
if (isComplexResult(result)) {
try {
thenable = result.then
if (typeof thenable === 'function') {
thenable.call(
result,
function (data) {
if (consumed) {
return
}
consumed = true
return resolvePromise(promise2, data, resolve, reject)
},
function (error) {
if (consumed) {
return
}
consumed = true
return reject(error)
}
)
} else {
resolve(result)
}
} catch (e) {
if (consumed) {
return
}
consumed = true
return reject(e)
}
} else {
resolve(result)
}
}
function LPromise(execute) {
this.status = 'pending'
this.value = null
this.reason = null
this.onFulfilledArray = []
this.onRejectedArray = []
const resolve = (value) => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status === 'pending') {
this.value = value
this.status = 'fulfilled'
this.onFulfilledArray.forEach((func) => func(value))
}
})
}
const reject = (reason) => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
if (this.status === 'pending') {
this.reason = reason
this.status = 'rejected'
this.onRejectedArray.forEach((func) => func(reason))
}
})
}
execute(resolve, reject)
}
LPromise.prototype.then = function (onFulfilled, onRejected) {
onFulfilled =
typeof onFulfilled === 'function'
? onFulfilled
: (data) => {
return data
}
onRejected =
typeof onRejected === 'function'
? onRejected
: (error) => {
throw error
}
let promise2
if (this.status === 'fulfilled') {
return (promise2 = new LPromise((resolve, reject) => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value)
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
}))
}
if (this.status === 'rejected') {
return (promise2 = new LPromise((resolve, reject) => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason)
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
}))
}
if (this.status === 'pending') {
return (promise2 = new LPromise((resolve, reject) => {
this.onFulfilledArray.push(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value)
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
this.onRejectedArray.push(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason)
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)
} catch (e) {
reject(e)
}
})
}))
}
}
|